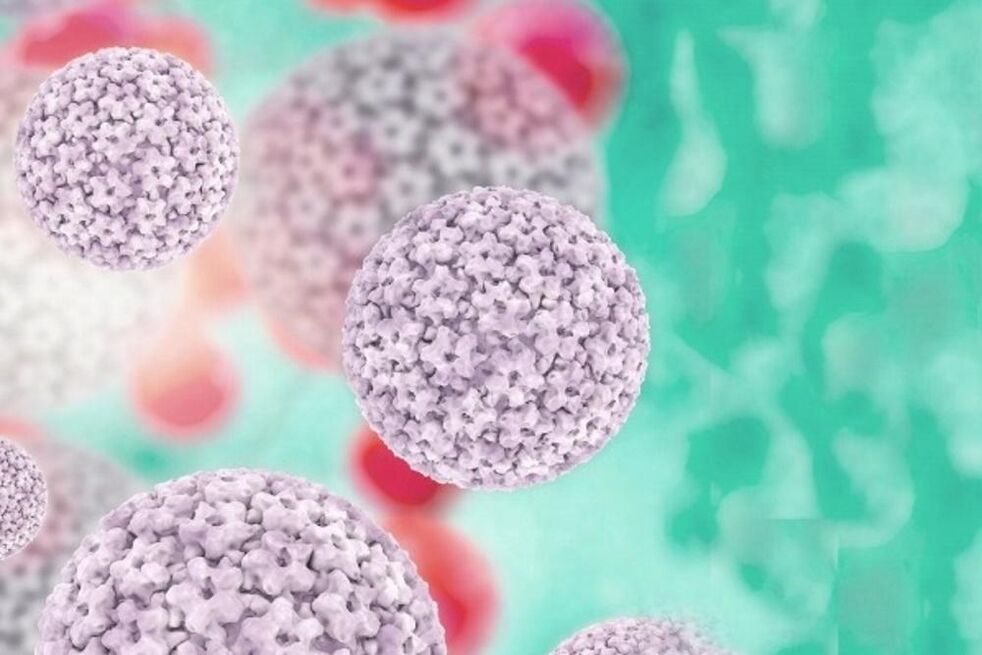
Human papillomavirus (HPV) affects epithelial cells and has a particle diameter of 55 nm. A characteristic feature is the proliferation of the skin epithelium, as well as the mucous membranes. In the initial stage, the pathogen usually affects the basal cells of the epithelium, penetrating them through microtraumas. Localized papillomas usually occur on the skin of the neck, armpits, groin and genitals (most commonly), the oral mucosa and the nasopharynx.
This virus can be asymptomatic for many years. Electron microscopic or molecularly hybridized methods are used to detect HPV.
Types of human papillomavirus
Humans have HPV, which affects the mucous membranes and skin. Among the large number of papillomaviruses there are species with low and high oncogenic risk. Oncogenic properties have been shown to be related to the ability to integrate DNA into the genome of human cells.
The virus is activated in 10-20% of cases. Depending on its type, this can lead to benign or malignant lesions. Some HPVs are not oncogenic. They lead to the appearance of warts and genital warts. The most common are HPV 6 and 11.
HPV oncogenes are those that have a high risk of developing cancerous lesions, especially of the cervix or anus. In terms of skin, HPV 16 and 18 are more common, as are HPV 5 and 8, which can lead to skin cancer. The most well-known form of HPV-induced cancer is cervical cancer. But men can also become infected with the papilloma virus, which in the worst cases causes cancer of the penis or anus.
Often women face HPV 16 - a form in which introsomal parasitism is observed, ie outside the cell chromosome (benign). HPV 18 is characterized by a high risk of developing oncology - first benign tumors form, which after some time degenerate into cancer. The virions in this case are small (up to 30 nm).
Different types of HPV infections lead to:
- neoplasms of the cervix;
- invasive or preinvasive oncology;
- genital warts of the urinary tract and genitals.
Ingestion of the pathogen in the body does not always lead to disease. It all depends on the predisposing factors: increased sexual activity, vitamin deficiency, pregnancy, hypothermia, endometriosis, smoking, alcohol abuse, etc. It should be noted that a viral infection can occur even in an organism with a good immune system.
Characteristics of the infection

The human papillomavirus is highly contagious. It is usually transmitted through direct contact, skin to skin or mucosa to mucosa, with an infected person. In genital infections, this most often occurs during vaginal or oral sex. A large number of sexual partners or other STIs (sexually transmitted infections) increase the risk. Indirect transmission through objects, contaminated clothing or bedding is also possible, but is rare.
In 7% of cases, mother-to-child transmission of the virus can occur during childbirth when the infection is active. The risk increases to 40% if you are infected with HPV 16 or 18.
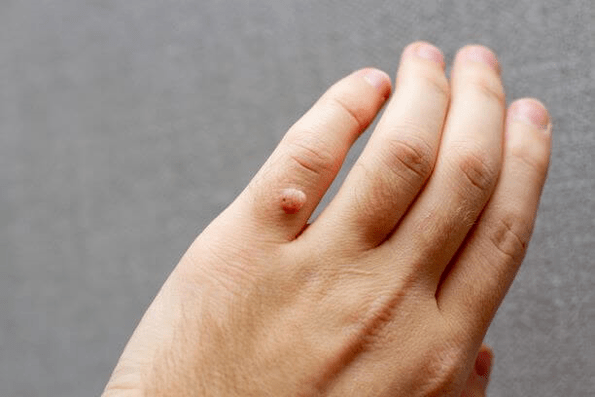
By penetrating the epithelium, disrupting the integrity, papillomavirus infection promotes the growth of the lower layer of epithelial cells in the form of warts or warts. This form of the disease is contagious and spreads rapidly to others. As a rule, warts and warts do not cause metastases and often disappear spontaneously.
Symptoms of HPV
The incubation period lasts up to 9 months (average 3 months). HPV can be present in the body without obvious symptoms. The virus can go unnoticed for months or years. Even at this stage, he is infected.
Skin warts usually appear in groups and increase with scratching. The two most common forms of papilloma are either grayish, hard, raised with a broken surface (common wart) or flat and reddish (flat wart). Acute warts are found on the feet or heels, grow inward and are therefore often painful.
The causes of genital warts are found on moist and warm parts of the body, which is why they are localized in the folds and on the mucous membranes. They can cause symptoms such as itching or burning. The incubation period, ie the time between infection and the onset of symptoms, in genital warts varies from 3 weeks to 8 months.
There are several forms of genital warts caused by different pathogens:
- Genital warts. Pale or reddish nodules that often stand in groups and appear on the labia, vagina, penis, urethra, anal canal and rectum. They are highly contagious.
- Flat warts. They appear in the form of flat nodules and are found mainly on the female genitals. They increase the risk of developing cancer.
- Giant warts (Buschke-Levenshtein tumors). They grow into huge formations, destroying the surrounding tissues. In rare cases, they can degenerate and lead to squamous cell carcinoma.

Infection of the mucous membranes in the upper respiratory tract is also possible. The conjunctiva of the eyes can be affected, leading to pink stem growths. It is more difficult to detect an asymptomatic course that the doctor can only see with the help of aids such as acetic acid (which causes discoloration of the warts) or a microscope.
In addition, the virus can also be found in cells without any tissue changes. Then they talk about a latent infection, ie the presence of pathogens, but without symptoms. After infection, this phase can last from a few weeks to several months.
Possible consequences
When infected, the viruses penetrate the cells of the integumentary tissue of the skin and mucous membranes, settle in the nuclei of cellular structures and multiply there. Usually, such HPV infections go unnoticed and treat themselves without sequelae, as the immune system successfully fights the pathogen.
However, some HPV types cause skin changes, ie growths. Possible forms include genital warts or warts and papillomas that can affect, for example, the face, arms or legs.
The tissue changes caused are mostly benign, but can also degenerate and lead to cancer. For example, cancer can occur decades after HPV infection. Cancers of the external female genitalia (cancer of the vulva and vagina), anal cancer, cancer of the penis and cancer of the mouth and throat (tumors of the head and neck) are also possible.
Diagnosis

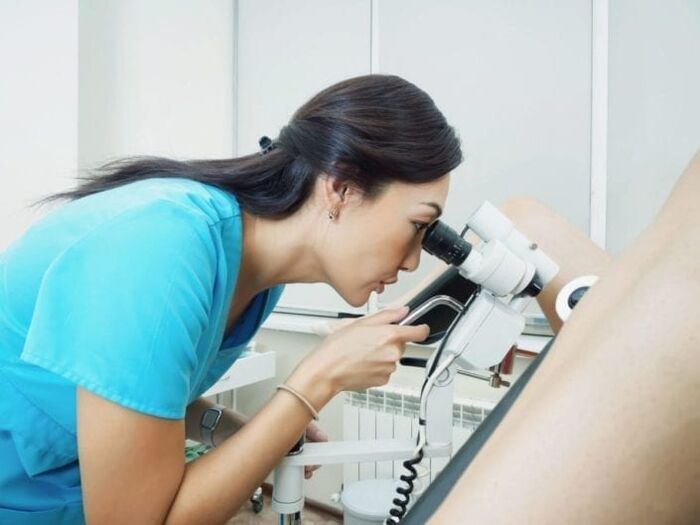
An HPV infection test is performed on women as part of preventive visits to the gynecologist. During a gynecological examination, a swab is taken from the lining of the cervix, this is called a Papanicolaou test (cytological examination). The resulting material is examined for tissue changes to determine precancerous conditions.
Alternatively, an HPV test may be performed in which cellular material from a mucosal swab or tissue sample is tested in a laboratory for certain viruses. However, this allows only the infection of the affected area to be proven, but not statements to be made as to whether tissue changes have occurred. Thus, the HPV test makes sense, especially when combined with a Pap test, and can help detect cancer precursors at an early stage.
If the test is positive, this is still not a cause for concern, as the infection does not always lead to cancer. Regular examination is recommended to detect tissue changes at an early stage. Conversely, a negative test result does not allow us to say whether there has been an infection in the past that the body has successfully fought.
In men, there is no prophylactic examination in which the test is performed regularly. If there is a corresponding cancer, the tumor test can determine if the HPV infection is at the root of the cancer.
Specialized DNA techniques are also used in laboratory diagnostics, such as real-time PCR. Anogenital warts caused by HPV types 6 and 11 are easily detected during a pelvic examination.
How to cure human papillomavirus

In most cases, the disease does not require treatment because it goes away on its own and then the viruses are no longer detected. However, if this is not the case, the infection can last longer and last for months or years.
To date, there are no methods for systemic exposure to this virus, so it would be possible to completely destroy it. However, treating the resulting warts reduces the number of viruses, so in many cases the immune system can fight other viruses and thus get rid of them. In some cases, pathogens survive and can cause symptoms over and over again.
Therapeutic tactics depend on the type of HPV and the associated picture of the disease:
- Plantar and genital warts can be treated with topical salicylic acid formulas.
- Cryotherapy is also a method often used for HPV. In this case, the wart is burned with cold, using liquid nitrogen.
- Lasers or electrocautery are equally applicable methods.
As the recurrence rate is quite high, it is advisable to check yourself regularly and use condoms even a few months after the lesions have disappeared, so as not to infect your sexual partner.
In HPV cancer, treatment is much more difficult. In cervical cancer, it is often advisable to remove the uterus, the upper part of the vagina and the ovaries, respectively. This can be supplemented with radiation therapy to rule out the possibility of recurrence. Other cancers caused by HPV are most often treated with targeted therapy, such as radiation or chemotherapy.
It should be remembered that surgery is not a cardinal solution, but only solves a cosmetic problem, because after removal the virus can remain in the surrounding tissues and warts can reappear.
Prevention of infection
There are two vaccinations: bivalent HPV 16 and 18 and tetravalent HPV 6, 11, 16 and 18. Vaccination is recommended for all young girls aged 14 and over.
Vaccination does not protect against all types of HPV. Therefore, regular check-ups are recommended for all women between the ages of 25 and 65, even if they have been vaccinated.
Timely detection and complete removal of genital warts reduces the risk of disease. The effectiveness of using condoms to prevent the transmission of infection can significantly reduce the risk of developing this condition. The most promising method for the prevention and treatment of the early stages of the disease caused by this infection is a specific multivalent vaccine.














































































